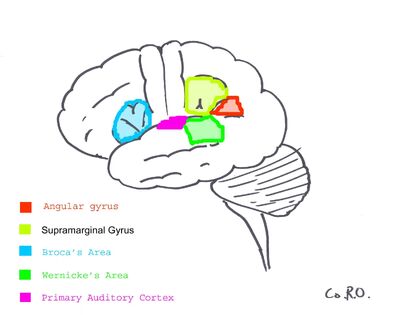
Figure one illustrates significant language areas of the brain. The arcuate fasciculus links the green area (Wernicke's) to the blue area (Broca's), disruption of this pathway results in conduction aphasia.
The arcuate fasciculus (Latin, curved bundle) is the neural pathway connecting the posterior part of the temporoparietal junction with the frontal cortex in the brain. In the cerebral hemisphere specialised for language, this pathway is thought to connect Broca's area to Wernicke's area.
It is thought to connect areas of the brain involved in the generation and understanding of language. Damage to this pathway can cause a form of aphasia known as conduction aphasia, where auditory comprehension and speech articulation are preserved, but people find it difficult to repeat heard speech.
See also[]
External links[]
Assessment |
Biopsychology |
Comparative |
Cognitive |
Developmental |
Language |
Individual differences |
Personality |
Philosophy |
Social |
Methods |
Statistics |
Clinical |
Educational |
Industrial |
Professional items |
World psychology |
Biological: Behavioural genetics · Evolutionary psychology · Neuroanatomy · Neurochemistry · Neuroendocrinology · Neuroscience · Psychoneuroimmunology · Physiological Psychology · Psychopharmacology (Index, Outline)
| This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia (view authors). |