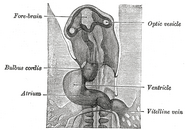
Brain: Forebrain
Diagram depicting the main subdivisions of the embryonic vertebrate brain. These regions will later differentiate into forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain structures.
[[Image:|250px|center|]]
Latin '
Gray's subject #
Part of
Components
Artery
Vein
BrainInfo/UW -
MeSH [1]
In the anatomy of the brain of vertebrates , the prosencephalon (or forebrain ) is the rostral -most (forward-most) portion of the brain . The prosencephalon, the mesencephalon (midbrain), and rhombencephalon (hindbrain) are the three primary portions of the brain during early development of the central nervous system . It controls body temperature, reproductive functions, eating, sleeping, and any display of emotions.
At the five-vesicle stage, the prosencephalon separates into the diencephalon (prethalamus, thalamus , hypothalamus , subthalamus , epithalamus , and pretectum ) and the telencephalon (cerebrum ). The cerebrum consists of the cerebral cortex , underlying white matter , and the basal ganglia .
When the embryonic prosencephalon fails to divide the brain into two lobes, it results in a condition known as holoprosencephaly .
Additional images [ ]
Embryo between eighteen and twenty-one days.
Head of chick embryo of about thirty-eight hours’ incubation, viewed from the ventral surface. X 26
See also [ ]
Telencephalon cerebral cortex , cerebral hemispheres ) - edit
primary sulci/fissures :medial longitudinal , lateral , central , parietoöccipital , calcarine , cingulate
frontal lobe :precentral gyrus (primary motor cortex , 4 ), precentral sulcus , superior frontal gyrus (6 , 8 ), middle frontal gyrus (46 ), inferior frontal gyrus (Broca's area , 44 -pars opercularis , 45 -pars triangularis ), prefrontal cortex (orbitofrontal cortex , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 47 )
parietal lobe :postcentral sulcus , postcentral gyrus (1, 2, 3, 43 ), superior parietal lobule (5 ), inferior parietal lobule (39 -angular gyrus , 40 ), precuneus (7 ), intraparietal sulcus
occipital lobe :primary visual cortex (17), cuneus , lingual gyrus , 18 , 19 (18 and 19 span whole lobe)
temporal lobe :transverse temporal gyrus (41-42-primary auditory cortex ), superior temporal gyrus (38 , 22 -Wernicke's area ), middle temporal gyrus (21 ), inferior temporal gyrus (20 ), fusiform gyrus (36 , 37 )
limbic lobe /fornicate gyrus :cingulate cortex /cingulate gyrus , anterior cingulate (24 , 32 , 33 ), posterior cingulate (23 , 31 ), isthmus (26 , 29 , 30 ), parahippocampal gyrus (piriform cortex , 25 , 27 , 35 ), entorhinal cortex (28 , 34 )
subcortical/insular cortex rhinencephalon , olfactory bulb , corpus callosum , lateral ventricles , septum pellucidum , ependyma , internal capsule , corona radiata , external capsule
hippocampal formation :dentate gyrus , hippocampus , subiculum
basal ganglia : striatum (caudate nucleus , putamen ), lentiform nucleus (putamen , globus pallidus ), claustrum , extreme capsule , amygdala , nucleus accumbens
Some categorizations are approximations, and some Brodmann areas span gyri.