Assessment |
Biopsychology |
Comparative |
Cognitive |
Developmental |
Language |
Individual differences |
Personality |
Philosophy |
Social |
Methods |
Statistics |
Clinical |
Educational |
Industrial |
Professional items |
World psychology |
Biological: Behavioural genetics · Evolutionary psychology · Neuroanatomy · Neurochemistry · Neuroendocrinology · Neuroscience · Psychoneuroimmunology · Physiological Psychology · Psychopharmacology (Index, Outline)
| Nerve: Nodose | ||
|---|---|---|
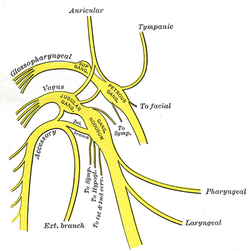
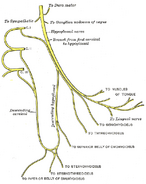
| Plan of upper portions of glossopharyngeal, vagus, and accessory nerves. ("Gang. nodosum" visible at center.) | ||
| [[Image:|250px|center|]] | ||
| Latin | ganglion nodosum, ganglion inferius nervi vagi. | |
| Gray's | subject #205 911 | |
| Innervates | ||
| From | vagus nerve | |
| To | ||
| MeSH | A08.340.390.550 | |
The nodose ganglion (ganglion of the trunk; inferior ganglion of vagus nerve) is cylindrical in form, of a reddish color, and 2.5 cm. in length.
Passing through it is the cranial portion of the accessory nerve, which blends with the vagus below the ganglion.
As opposed to the jugular ganglion of the vagus nerve, the inferior or nodose ganglion is larger.
It is chiefly visceral afferent in function concerning sensation of heart, larynx, lungs and alimentary tract from the pharynx to the transverse colon.
Both ganglia are traversed by parasympathetic, and perhaps some sympathetic fibres.
Preganglionic motor fibres (ganglionic branches) from the dorsal vagal nucleus and the special visceral efferents from the nucleus ambiguus, which descend to the inferior vagal ganglion form a band skirting the ganglion.
Additional images[]
External links[]
I-IV: olfactory - optic - oculomotor - trochlear
V: trigeminal: trigeminal ganglion
V1: ophthalmic: lacrimal - frontal (supratrochlear, supraorbital) - nasociliary (long root of ciliary, long ciliary, infratrochlear, posterior ethmoidal, anterior ethmoidal) - ciliary ganglion (short ciliary)
V2: maxillary: middle meningeal - in the pterygopalatine fossa (zygomatic, zygomaticotemporal, zygomaticofacial, sphenopalatine, posterior superior alveolar)
in the infraorbital canal/infraorbital nerve (middle superior alveolar, anterior superior alveolar)
on the face (inferior palpebral, external nasal, superior labial, infraorbital plexus) - pterygopalatine ganglion (deep petrosal, nerve of pterygoid canal)
branches of distribution (palatine, nasopalatine, pharyngeal)
V3: mandibular: nervus spinosus - medial pterygoid - anterior (masseteric, deep temporal, buccal, lateral pterygoid)
posterior (auriculotemporal, lingual, inferior alveolar, mylohyoid, mental) - otic ganglion - submandibular ganglion
VI: abducens
VII: facial: nervus intermedius - geniculate - inside facial canal (greater petrosal, nerve to the stapedius, chorda tympani)
at exit from stylomastoid foramen (posterior auricular, digastric - stylohyoid)
on face (temporal, zygomatic, buccal, mandibular, cervical)
VIII: vestibulocochlear: cochlear (striae medullares, lateral lemniscus) - vestibular
IX: glossopharyngeal: fasciculus solitarius - nucleus ambiguus - ganglia (superior, petrous) - tympanic - carotid sinus
X: vagus: ganglia (jugular, nodose) - Alderman's nerve - in the neck (pharyngeal branch, superior laryngeal ext and int, recurrent laryngeal)
in the thorax (pulmonary branches, esophageal plexus) - in the abdomen (gastric plexuses, celiac plexus, gastric plexus)
XI: accessory XII: hypoglossal